Lung cancer progression - Pre-treatment
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
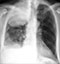
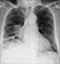
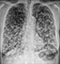
Lung cancer progression - Pre-treatment
- This long term smoker presented with a cough and finger clubbing
- A large lobulated mass is seen in the region of the right lung hilum - proven to be a cancer following biopsy
- CT showed it was non-operable and chemotherapy was offered
Lung cancer - Post-chemotherapy
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
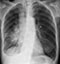
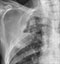
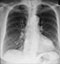
Lung cancer - 3 months post-chemotherapy
- The mass can no longer be seen clearly indicating a good response to treatment
- The raised position of the right hemi-diaphragm is a sinister feature and implies injury or invasion of the phrenic nerve leading to phrenic nerve palsy
Lung cancer - 4 months after chemotherapy
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
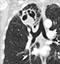
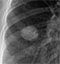
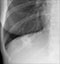
Lung cancer - 4 months after chemotherapy
- The mass has recurred
- Consolidation seen distal to the mass (asterisks) may be due to disease infiltration, lymphangitis or possibly infection
- This consolidation is demarcated inferiorly by the horizontal fissure indicating it is mainly in the right upper lobe
- The right hemi-diaphragm is higher than on the previous image indicating increasing volume loss of the right lung
- Blunting of the right costophrenic angle indicates a pleural effusion
- Bulging of the left mediastinal contour indicates progression of disease through the mediastinum to the contralateral side
Lung cancer - Disease progression
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
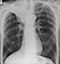
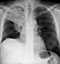
Lung cancer - Disease progression
- Another month later the mass has again increased in size
- The horizontal fissure is displaced superiorly - indicating the right upper lobe has lost volume due to occlusion of airways
- Increased density (whiteness) under the level of the diaphragm indicates the presence of pleural fluid – this is the typical appearance of a subpulmonic effusion (fluid located between the lung base and hemidiaphragm)
Lung cancer - Disease progression
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
Lung cancer - Disease progression
- After a further month the mass and effusion have again increased in size
- There is now a contralateral pleural effusion