Primary TB
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
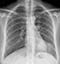
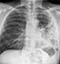
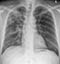
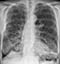
Primary TB
- There are no radiological features which are in themselves diagnostic of primary mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (TB) but a chest X-ray may provide some clues to the diagnosis
- This image shows consolidation of the upper zone with ipsilateral hilar enlargement due to lymphadenopathy
- These are typical features of primary TB
- Note: The chest X-ray may be normal in primary TB, in fact most patients infected are never unwell enough to require a chest X-ray
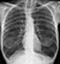
Healed primary TB
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
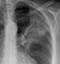
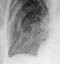
Healed primary TB
- Following an immune response to primary infection, a caseating granuloma forms which calcifies over time – this is known as a ‘Ghon focus’ – TB has gone!
- A Ghon focus is a rounded, well-defined focus of calcific density (as dense as bone) usually located in the periphery of the lung
- This chest X-ray shows a large, rounded calcified focus near the right hilum
- The CT (not usually necessary) shows it is located in the lung peripherally
- This is a particularly large Ghon focus
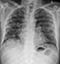
Post-primary TB
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
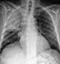
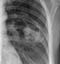
Post-primary TB
- Post-primary TB (secondary TB or reactivation TB) is more common in immunocompromised individuals – for example those with HIV/AIDS, those on immunosuppressing drugs, or those with malnutrition or diabetes
- The upper lobes are more commonly affected
- Consolidation often extends to the hilum
- The hilar structures may be distorted due to volume loss of the upper lobe
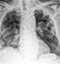
Post-primary TB – Lung cavity
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
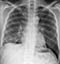
Post-primary TB – Lung cavity
- (Same patient as image above – 4 months later)
- Cavities are a common finding in mycobacterial infection
Healed post-primary TB
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
Healed post-primary TB
- Following an immune response to post-primary infection, the affected area often becomes scarred (fibrotic) and calcified
- The combined fibrosis and calcification can be described as ‘fibro-calcific change’
Miliary TB
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
Miliary TB
- Miliary TB is due to disseminated spread of mycobacterial infection
- It can occur either at the time of primary infection or on disease reactivation – prognosis is poor
- Very fine nodules are typically seen scattered throughout the lungs